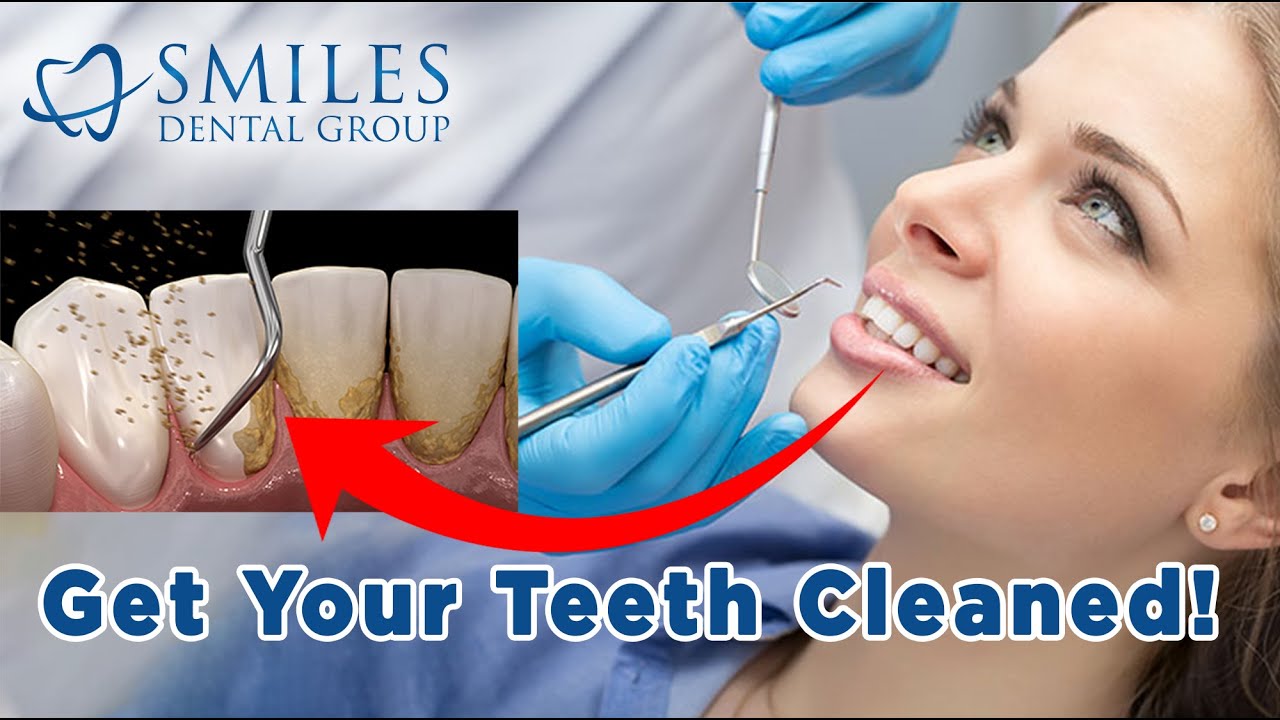
What is Gum disease?
Gum disease usually happens as a result of poor oral care, the bacteria in your mouth will infect your gums causing a wide range of symptoms. In the early stages, it can be reversabile at home, but if periodontitis occurs you will need a dental proffesional to treat it.Fast Facts Gingivitis
- A periodontist specialty is gum disease, mainly advanced periodontitis.
- There are 4 stages of gum disease, only gingivitis is 100% reversible.
- Having proper oral care and a balanced diet is a great defense against gingivitis.
Many patients are afflicted with gingivitis and they may not even realize it. One of the biggest indicators of infected gums is bleeding puffy gums. If your gums bleed from any or no agitation, then there’s a good chance you have some degree of gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis may eventually turn into periodontitis, which can get bad enough to require a specialist to repair the damage.
Gingivitis – What is it?
Periodontitis – What is it?
Gingivitis & periodontitis – Why does it happen?
Your gums attach themselves directly to your teeth, they are actually attached at a lower point than what is visible. The point of attachment forms a small space called a sulcus, this pocket can actually trap food and plaque, which will eventually turn into tartar. Once enough food and plaque are trapped in the gum pocket, it can start to force the gums away from the teeth. Once this starts to occur, you can even begin to lose teeth (they may just loosen & or fall out), in very extreme cases you can even lose bone.
Summary – Why does gingivitis happen?
Mostly from plaque, bacteria, and food buildup. This will cause the gums to be pushed further away from your teeth resulting in further complications.

Who’s at risk for gingivitis and periodontitis?
- Smoking or chewing tobacco
- Diabetes
- Consuming certain medications (ask your dentist)
- Crooked teeth
- Poorly fitted dental appliances
- Broken fillings
- Pregnancy
- Genetic factors
- Compromised immunity such as with HIV/AIDS
Summary – Who is at risk?
Everybody is at risk, there are certain factors that can make you more prone to gum disease, like bad oral care or an unbalanced diet.
Does gum disease have any signs or symptoms?
- Red, tender, or swollen gums.
- Gums that bleed when they are flossed or brushed.
- Unexplained loose teeth.
- A change in your bite (malocclusion)
- Pus between your teeth and gums, or while chewing
- Overly sensitive teeth/or pain while chewing.
- Dentures that no longer fit
- Stubborn bad breath (halitosis)
How Are Gingivitis And Periodontitis Diagnosed?
Summary – How is gum disease diagnosed?
Gum disease has lots of early warning signs, however, it may be difficult to tell if it’s advanced before it’s too late.
4 distinct stages of gum disease
Gingivitis
Slight Periodontal Disease
Moderate Periodontal Disease
Advanced Periodontal Disease
Summary – 4 distinct phases
- Gingivitis – Bacteria & plaque build-up, this is reversible.
- Slight Periodontal Disease – Bacteria has reached the bone, no longer reversible
- Moderate Periodontal Disease – The bacteria has become more aggressive, bone loss is now a risk.
- Advanced Periodontal Disease – Bone loss is now a serious risk, other health complications may occur.
How can you treat gum disease?
In the early stages of gingivitis, it can be a very easy affliction to reverse. Here are some things you can do if you are affected by mild gingivitis.
- Better/more frequent oral care
- Stop smoking/using tobacco products
- Stop smoking marijuana products (any smoke is bad for teeth)
- Eat less sugar and carb-heavy foods (bacteria eat carbs which produce plaque as a bi-product)
- Drink less alcohol
- Don’t eat after your last brush before you go to bed
How can you treat advanced gingivitis or periodontitis?
- Deep cleaning your teeth
- Antibiotic medications
- Surgery
Summary – How can you treat gum disease?
Ask your dentist for dental care routine tips and healthy living advice. Advanced gum disease needs to be treated at the dental clinic with advanced techniques.
How can gum disease be prevented?
Gingivitis can be prevented right at home through your regular oral care routine. Here are a couple of tips on how you can prevent gingivitis:
- Increase your brushing, flossing, and mouthwash frequency
- Go for a bi-annual (twice a year) checkup
- Eat a balanced diet
Frequently asked questions
Absolutely! Your gums can get puffy and bleed, you may not feel any pain at all. If you notice signs of gum disease, please get it checked even if there is no pain.
If it’s very advanced you may need to see a specialist, although, a general dentist will be able to handle most cases.
It depends on how advanced the gingivitis is. You will want to get your dentists advice before trying to take care of it yourself.